Coeus: Accelerating Scientific Insights Using Enriched Metadata
Coeus is a context-aware active storage framework designed to accelerate large-scale scientific data analysis by computing derived quantities in-transit during data production. Implemented as an Adios2 plugin engine and integrated with the Hermes hierarchical buffering platform, Coeus reduces I/O bottlenecks, minimizes unnecessary data movement, and improves time-to-insight for scientific workflows.
In collaboration with Sandia and Oak Ridge National Laboratories, Coeus investigates the use of an active storage system to calculate derived quantities and support complex queries on scientific data (simulation and observational) as well as optimizing data placement across the storage hierarchy, with awareness of the resource limitations, to better support the scientific discovery process.
Project Scope and Vision
Project Goals
Coeus focuses on:
- Active in-transit derivation of scientific quantities to avoid repetitive post-processing I/O
- Intelligent hierarchical storage for both raw and derived data to optimize retrieval latency
- Context-aware data placement informed by high-level I/O patterns
- Flexible, SQL-enabled querying over enriched metadata to accelerate data discovery
- Transparent integration with existing Adios2-based workflows
Vision
Coeus envisions an active storage architecture where scientific insights are computed and stored alongside raw data during simulation, reducing expensive I/O operations and enabling faster, more interactive analysis phases.
Key Challenges in Scientific Data Analysis
- High I/O Cost in Analysis Phase – Scientific queries often require scanning massive datasets multiple times
- Redundant Data Movement – Raw data is frequently moved and transformed unnecessarily before analysis
- Underutilized Storage Hierarchies – Deep HPC storage tiers are not optimally managed for analysis workloads
- Limited Query Capabilities – Existing HPC I/O libraries lack expressive querying on derived data
- Metadata Bottlenecks – Large-scale metadata operations stress PFS metadata servers
- Workflow Separation – Strict producer/consumer phases increase time-to-insight
Objectives and Architecture Overview
Core Objectives
- Provide human-readable mathematical language (HDCalc) for defining derived quantities
- Enable efficient extraction of insights from raw and derived data via enriched metadata
- Use context-aware hierarchical storage management for optimal data placement and prefetching
- Avoid slowing simulations by mediating resource contention between production and analysis
High-Level Architecture
Coeus extends the Adios2 I/O pipeline with:
- Semantic Derived Quantity Language → Compiles equations into an Operation Graph (OpGraph) for optimized execution
- Hierarchical Storage Manager → Uses Hermes to place and reorganize data blobs based on access patterns
- Metadata Engine → Stores operational and enriched metadata in SQLite for fast queries
- Query API → Supports range queries, bounding box searches, and derived quantity retrieval
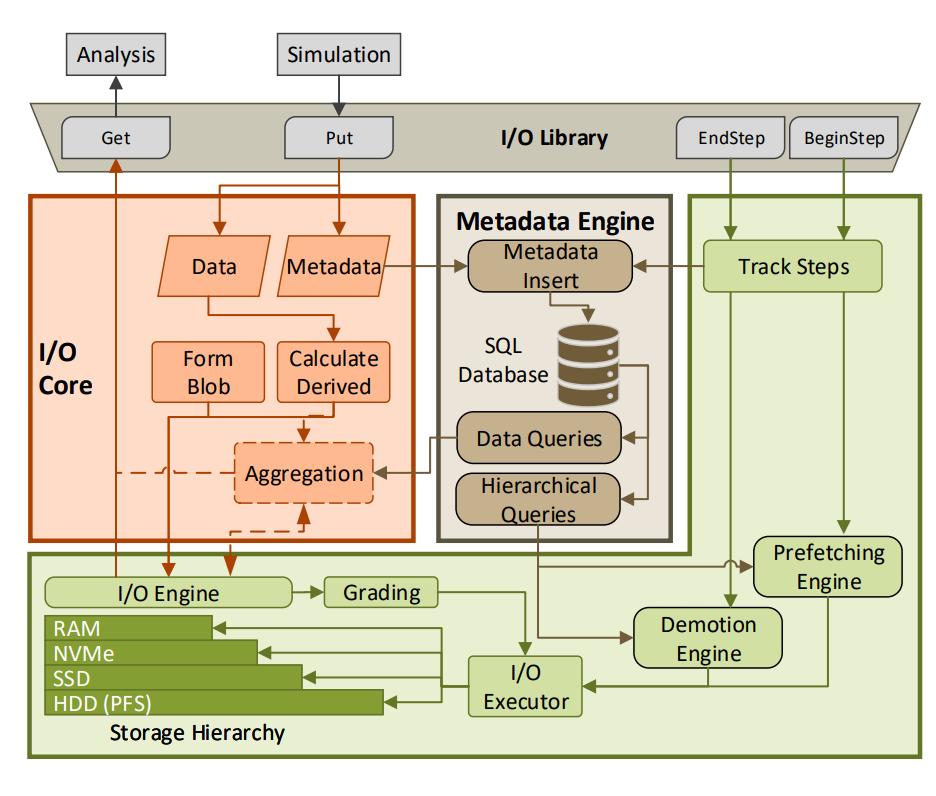
Technical Architecture
Semantic Derived Quantity Language
Semantic Derived Quantity Language supports:
- Arithmetic operations, aggregation, filtering, and statistics
- Integrals, derivatives, and mathematical macros
- Equations compiled into OpGraphs with explicit data dependencies
Example: Precomputing probability hash functions in the scientific simulation
Metadata Management
Operational Metadata – Automatically tracked variable information (type, dimensions, offsets)
Enriched Metadata – User- or system-generated annotations (threshold tags, bounding boxes, statistics)
Stored in SQL database for fast, expressive queries
Hierarchical Storage Optimization
Blob Scoring Algorithm considers:
- Task dependencies
- Access frequency & recency
- Prefetch predictions
- Application-specific priorities
Context-Aware Prefetching informed by Adios2 step patterns
Dynamic Reorganization to promote/demote data based on changing workflow needs
Implementation Details
Adios2 Integration
Coeus is implemented as an Adios2 plugin engine, providing seamless integration with existing scientific workflows. The plugin architecture allows:
- Transparent derivation of quantities during data production
- Minimal performance impact on simulation phases
- Flexible deployment across different storage backends
Hermes Integration
Integration with the Hermes hierarchical buffering platform enables:
- Intelligent data placement across storage tiers
- Context-aware prefetching based on access patterns
- Dynamic reorganization of data based on workflow requirements
Query Capabilities
Coeus provides advanced querying capabilities including:
- Range Queries – Efficient retrieval of data within specified ranges
- Bounding Box Searches – Spatial queries for multi-dimensional data
- Derived Quantity Retrieval – Direct access to precomputed insights
- SQL-enabled Interface – Familiar query language for scientific users
Use Cases and Applications
Scientific Simulations
Coeus is particularly effective for:
- Computational Fluid Dynamics – Real-time derivation of flow statistics
- Molecular Dynamics – In-transit calculation of structural properties
- Climate Modeling – Active computation of derived climate indices
- Particle Physics – Real-time analysis of collision data
Data Analysis Workflows
The framework supports:
- Interactive Analysis – Fast query response for exploratory data analysis
- Batch Processing – Efficient handling of large-scale analysis tasks
- Real-time Monitoring – Continuous derivation of key metrics during simulation
Latest Progress
We are implementing the Coeus engine into ParaView and Catalyst to facilitate enhanced data movement and metadata management for in-situ visualization workflows.
Collaborators
- Sandia National Laboratories
- Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Sponsor

This research is supported by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) through collaborative research initiatives with Sandia and Oak Ridge National Laboratories.