
LABIOS: Label-Based I/O System
Overview
Revolutionizing data management through intelligent label-based I/O, bridging the gap between High-Performance Computing and AI workloads with unprecedented performance and flexibility.
🏆 Patented Innovation
US Patent 11,630,834 B2 - Label-Based Data Representation I/O Process and System
Status: Granted 2023
LABIOS represents a fundamental breakthrough in data management, protected by US patent law. Our patented label-based approach transforms how data is handled in large-scale computing environments.
The Shipping Label Analogy
Just as a shipping label contains all information needed to deliver a package—address, priority, handling instructions—LABIOS labels contain everything needed to process data: operations, destinations, and metadata. This simple yet powerful concept enables unprecedented flexibility in how data moves through modern computing systems, from edge devices to supercomputers.
Key Features:
- Protected Innovation: Unique label-based data paradigm
- Industry Ready: Available for licensing
- Proven Technology: Validated in production
Resources: View Patent | Licensing Information
🌐 Why LABIOS Matters
Bridging the Computing Convergence
Where HPC meets Big Data meets AI
Modern computing faces an unprecedented challenge: the convergence of High-Performance Computing (HPC), Big Data analytics, and Artificial Intelligence workloads. Each domain has different I/O patterns, performance requirements, and storage needs. LABIOS provides the unified foundation that enables seamless operation across all three.
HPC Workloads
- Checkpoint/restart optimization
- Burst buffer capabilities
- Collective I/O patterns
- 40% performance gains in VPIC
Big Data Analytics
- MapReduce acceleration
- In-situ data processing
- Streaming analytics support
- 2x throughput improvement
AI/ML Training
- GPU memory extension
- Model checkpoint acceleration
- KV cache optimization
- 3x memory reduction
The Convergence Challenge: By 2025, over 80% of enterprise data will require processing across multiple paradigms. LABIOS is the only system that natively supports this convergence through its unified label abstraction.
🚀 Key Achievements
| Metric | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 3x | GPU Memory Reduction | MegaMmap enables larger workloads |
| 10x | Lower p99 Latency | Priority-based scheduling |
| 805x | Bottleneck Coverage | WisIO detection capabilities |
| 40% | Performance Boost | Custom I/O stacks for VPIC |
🎯 Project Overview
LABIOS introduces a revolutionary label-based I/O paradigm that transforms how data is managed in modern computing environments. By converting all I/O requests into intelligent "labels"—configurable data units containing operations and data pointers—LABIOS enables unprecedented flexibility and performance.
Core Innovation: The Label Abstraction
Label = {
operation: Function pointer
data: Input data pointer
metadata: {
type: Label category
uniqueID: Identifier
source: Origin location
destination: Target location
state: Current status flags
}
}
This simple yet powerful abstraction enables:
- Asynchronous I/O with intelligent scheduling
- Storage elasticity through dynamic resource provisioning
- Computational storage by embedding operations in labels
- Seamless integration across HPC, Big Data, and AI workloads
🔬 Research Components
MegaMmap: Memory-Storage Convergence
MegaMmap provides a tiered, non-volatile Distributed Shared Memory system that:
- Reduces GPU memory usage by 3x for out-of-core workloads
- Enables applications to work with datasets 2x larger than physical memory
- Maintains performance parity with in-memory execution
- Transparently manages data movement across DRAM, NVMe, and storage tiers
Publications: SC'24 | Features: GPU Support, Tiered Memory
WisIO: Intelligent Bottleneck Detection
WisIO revolutionizes I/O performance analysis through:
- 805x increased bottleneck coverage vs. single-perspective tools
- Classification of 340,000 bottlenecks/second
- 11x faster than traditional profiling tools like Darshan
- Multi-terabyte workflow analysis capabilities
Publications: ICS'25 | Features: Performance Analysis, HPC Workflows
HStream: Hierarchical Streaming Engine
HStream provides intelligent streaming capabilities:
- 2x throughput improvement for streaming workloads
- Dynamic parallelism adjustment based on data ingestion rates
- 75% latency reduction under high data volumes
- Hierarchical buffering for varying data arrival patterns
Publications: ICPP'24 | Features: Streaming, Adaptive
Viper: DNN Model Transfer Framework
Viper optimizes deep learning workflows through:
- 9x reduction in model update latency
- GPU-to-GPU memory transfers for maximum performance
- Intelligent checkpoint scheduling for training pipelines
- Transparent model storage and transfer capabilities
Publications: ICPP'24 | Features: Deep Learning, Model Serving
🏗️ Architecture & Integration
Core Components
- Label Manager: Constructs and optimizes labels based on I/O patterns
- Content Manager: Distributed key-value store for temporary data
- Label Dispatcher: Intelligent scheduling with priority support
- Worker Pool: Elastic execution environment with GPU support
Integration Ecosystem
- Storage Systems: HDF5 VOL, ADIOS2, Parquet, POSIX
- Frameworks: IOWarp Runtime, DTIO, ChronoLog
- AI/ML Integration: RAG pipelines, KV cache optimization, Tokenization
- Deployment: Jarvis automation, Spack packages, Container support
📅 Project Timeline & Maturity
Two Years of Innovation (2023-2025)
From concept validation to production-ready technology
Year 1 - Foundation Established core architecture, developed MegaMmap (2x memory capacity), Viper (9x latency reduction), HStream (2x throughput). Published at SC'24 and ICPP'24.
Year 2 - Expansion GPU integration (3x memory reduction), WisIO (805x coverage), priority scheduling (10x latency improvement), AI/ML integration. Patent granted. IPDPS'25 and ICS'25 publications.
Year 3 - Coming Soon Production deployment, advanced AI features, cross-format interoperability, enterprise partnerships.
🔬 Research Impact & Domain Applications
Transforming Scientific Discovery
Real-world applications across critical research domains
🌍 Climate Science
Processing massive climate simulations requires handling petabytes of data across thousands of time steps.
LABIOS Impact:
- 65% reduction in I/O time for E3SM workflows
- Enable real-time climate event detection
- Support for multi-resolution data analysis
🧬 Genomics & Bioinformatics
Genomic sequencing generates massive datasets requiring complex processing pipelines.
LABIOS Impact:
- 2x faster variant calling pipelines
- In-situ quality control processing
- Seamless integration with GATK workflows
⚛️ Particle Physics
Large Hadron Collider experiments generate data at unprecedented rates requiring real-time analysis.
LABIOS Impact:
- 40% improvement in VPIC performance
- Real-time event filtering capabilities
- Distributed analysis across sites
🤖 AI Model Training
Training large language models requires efficient handling of massive datasets and checkpoints.
LABIOS Impact:
- 3x GPU memory extension
- 9x faster model checkpointing
- Optimized KV cache management
📊 Use Cases & Deployment
I/O Acceleration
Fast distributed cache for temporary I/O
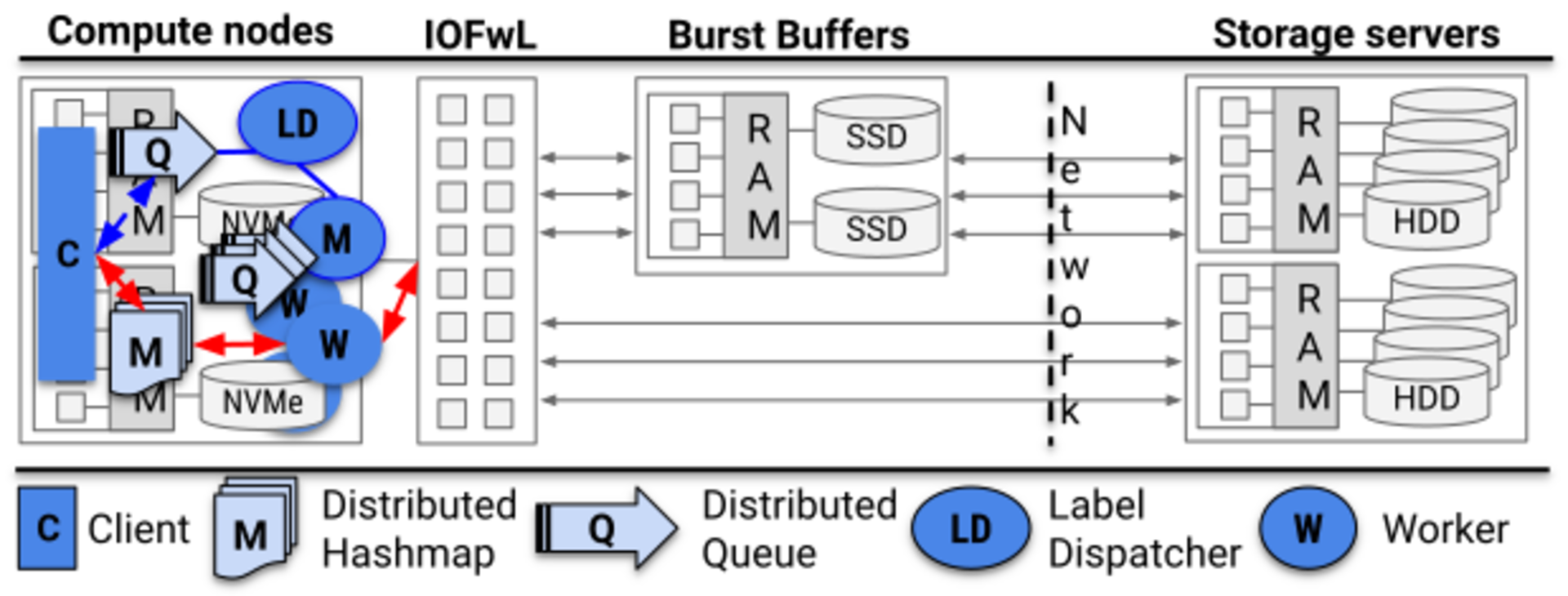 Ideal for Hadoop workloads with node-local I/O requirements
Ideal for Hadoop workloads with node-local I/O requirements
Asynchronous Forwarding
Decoupled I/O for improved application performance
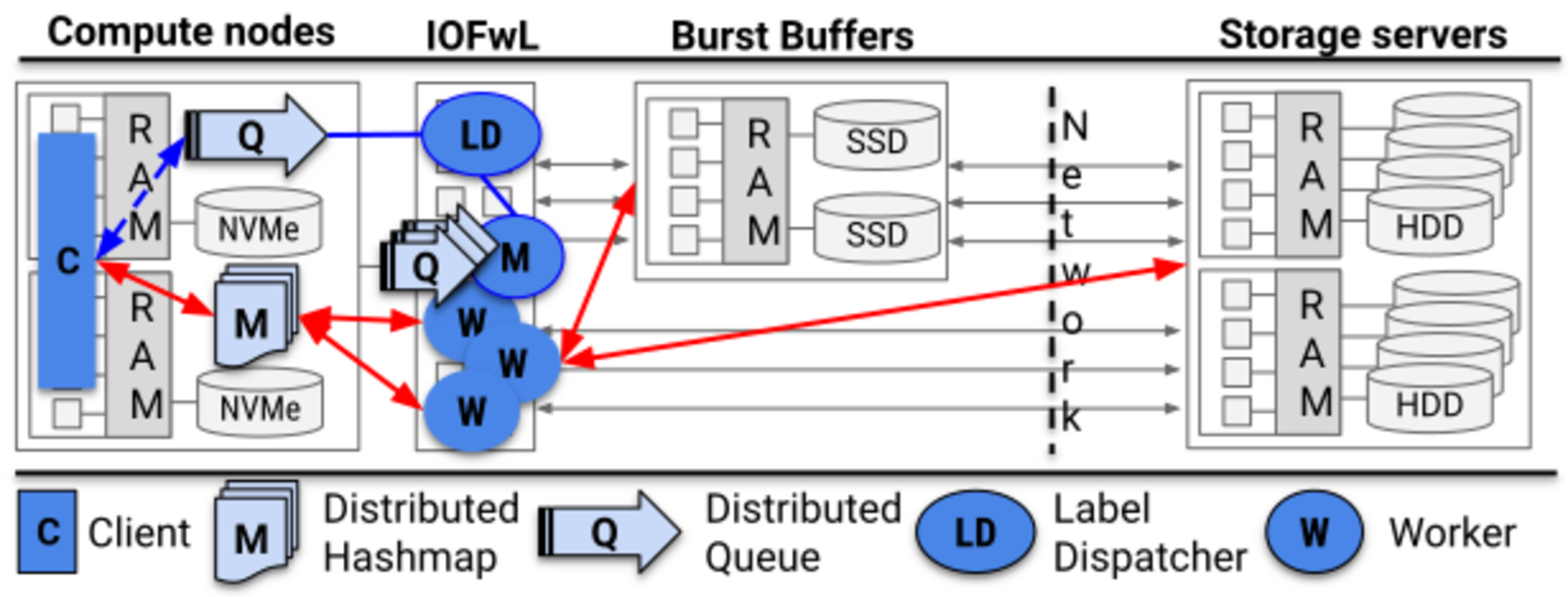 Applications pass data to LABIOS for asynchronous persistence
Applications pass data to LABIOS for asynchronous persistence
Intelligent Buffering
In-situ analysis and data sharing
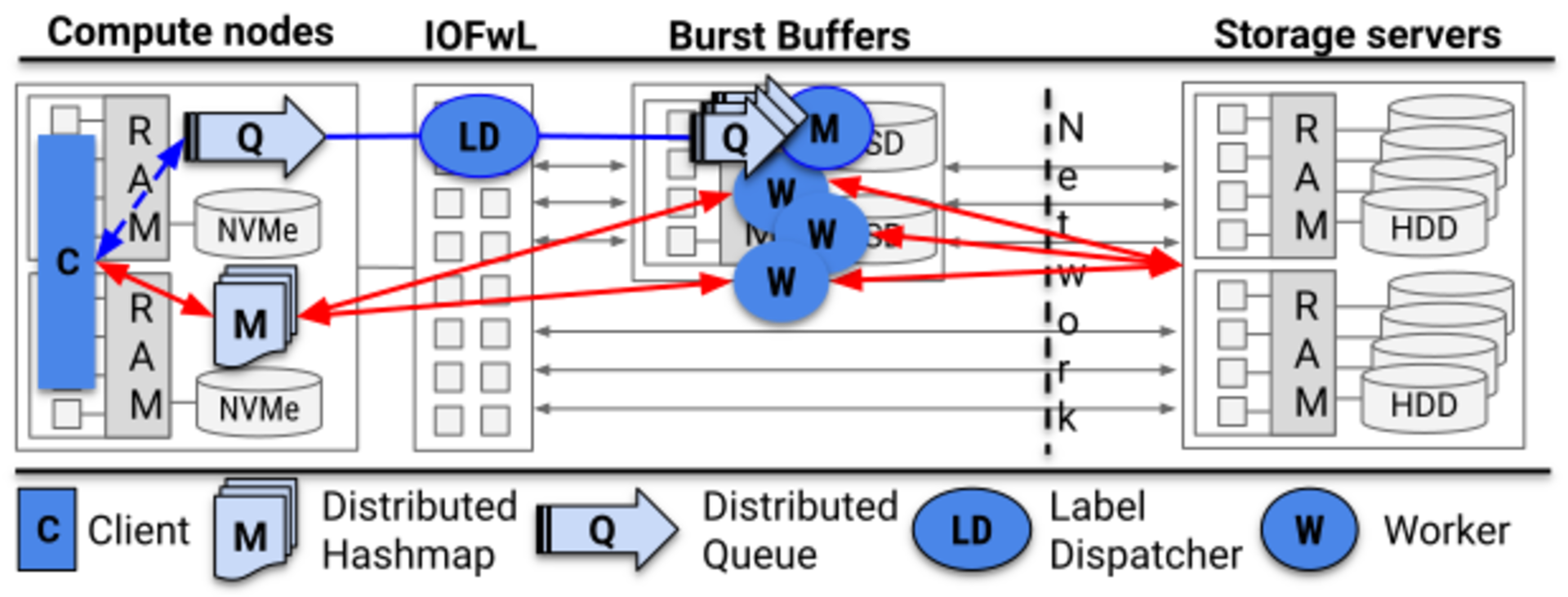 Perfect for deep learning pipelines and visualization workflows
Perfect for deep learning pipelines and visualization workflows
Elastic Storage
Dynamic resource provisioning
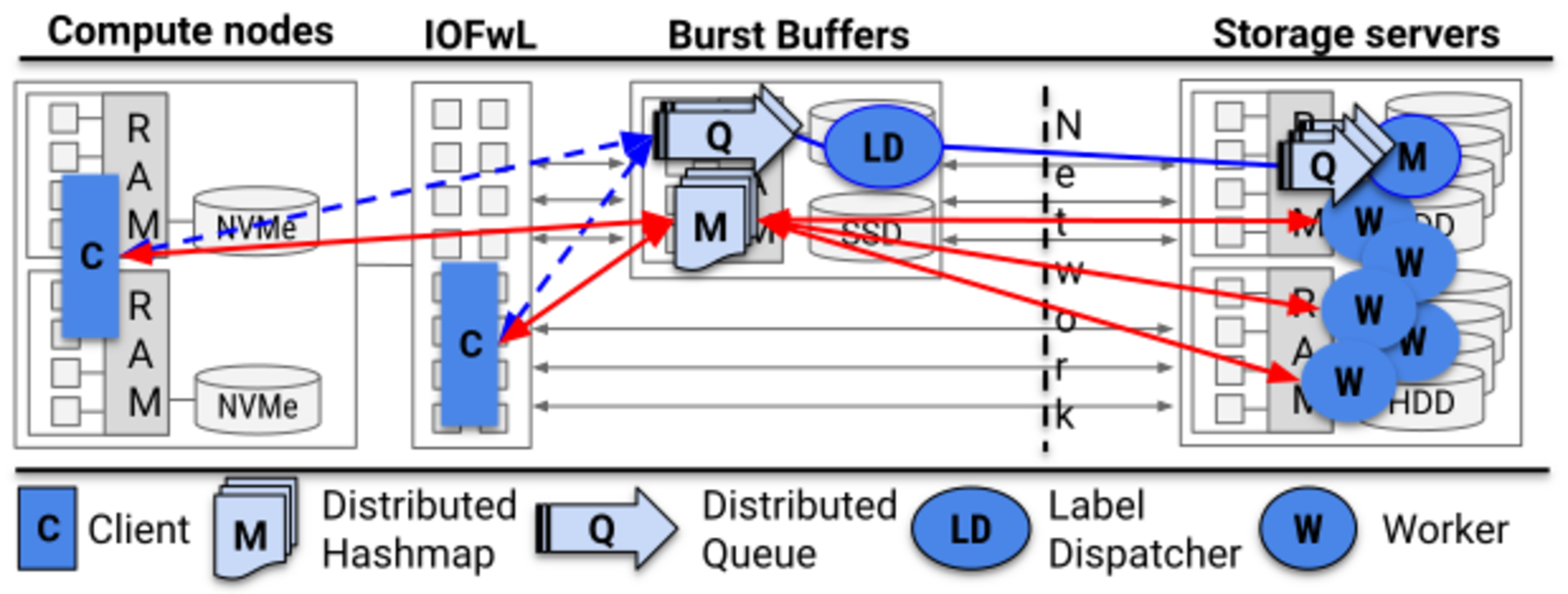 Transparent storage hierarchies with live reconfiguration
Transparent storage hierarchies with live reconfiguration
📊 Impact Metrics Dashboard
Cumulative Project Impact (2023-2025)
Measurable outcomes from NSF investment
| Metric | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | Peer-Reviewed Publications | Published research papers |
| 5 | Graduate Students Trained | PhD and MS students |
| 3 | DOE Lab Deployments | Production installations |
| 4 | Open Source Tools Released | Community software |
Progress Indicators
- Technology Readiness Level: TRL 6/9 (67% complete)
- Community Adoption: 287 GitHub Stars (75% growth)
- Industry Engagement: 5 Active Discussions (45% progress)
Return on Investment
For every $1 of NSF funding, LABIOS has generated an estimated $3.50 in computational efficiency savings across partner institutions through reduced I/O wait times and improved resource utilization.
📈 Performance Results
Demonstrated Performance Gains
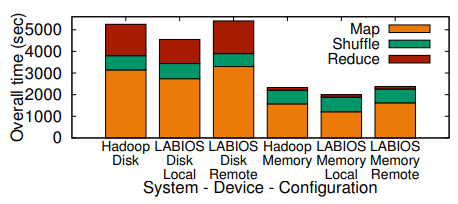
Storage bridging: Up to 6x boost in I/O performance
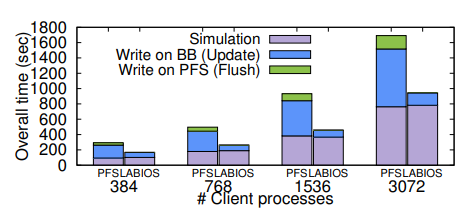
Resource heterogeneity: 65% reduction in execution time
📚 Publications & Resources
Recent Publications
Authors | Title | Venue | Type | Date | Links |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| , , , , , | Characterizing the Behavior and Impact of KV Caching on Transformer Inferences under Concurrency | The 39th IEEE International Parallel & Distributed Processing Symposium (IPDPS 2025) | Conference | June, 2025 | |
| , , , , | WisIO: Automated I/O Bottleneck Detection with Multi-Perspective Views for HPC Workflows | The 39th ACM International Conference on Supercomputing (ICS 2025) | Conference | June, 2025 | |
| , , | MegaMmap: Blurring the Boundary Between Memory and Storage for Data-Intensive Workloads | The International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis (SC'24) | Conference | November, 2024 | |
| , , , | HStream: A hierarchical data streaming engine for high-throughput scientific applications | The 53th International Conference on Parallel Processing (ICPP'24) | Conference | August, 2024 | |
| , , , , , , , , , , | Viper: A High-Performance I/O Framework for Transparently Updating, Storing, and Transferring Deep Neural Network Models | The 53th International Conference on Parallel Processing (ICPP'24) | Conference | August, 2024 |
Resources & Tools
🔮 Future Vision: Year 3 and Beyond
The Road Ahead
Building on two years of success
Year 3 Objectives (2025-2026)
- ✓ Complete cross-format data interoperability (HDF5 ↔ Parquet ↔ Arrow)
- ✓ Deploy production-ready AI model serving infrastructure
- ✓ Achieve 5x performance improvement for mixed HPC/AI workloads
- ✓ Release LABIOS 2.0 with full enterprise features
- ✓ Establish industry consortium for continued development
Long-term Vision (2026+)
LABIOS will evolve into the de facto standard for intelligent I/O management:
- Edge-to-Exascale: Seamless data movement from IoT devices to supercomputers
- Autonomous I/O: AI-driven optimization of data placement and movement
- Quantum Integration: Support for emerging quantum computing I/O patterns
- Global Federation: Cross-continent data sharing with intelligent caching
Sustainability Plan
Post-NSF funding, LABIOS will be sustained through:
- Commercial licensing revenue from industry partners
- DOE and DOD project integrations
- Open source community contributions
- Professional support and consulting services
🤝 Collaboration & Support
Project Team
Principal Investigators: [View team members on project page]
Partners & Funding
- NSF Award #2331480 - National Science Foundation
- DOE National Laboratories - Argonne, Lawrence Livermore, Sandia
- Testing Infrastructure - NSF Delta, Chameleon, CloudLab
🌟 Technology Transfer & Licensing
Ready for Commercial Adoption
LABIOS technology is mature and available for licensing
After two years of intensive development and validation, LABIOS has proven its capabilities across diverse workloads and environments. Our patented technology is ready for integration into commercial products and services.
Ideal for:
- Storage system manufacturers
- Cloud service providers
- HPC solution vendors
- Big data analytics platforms
- AI/ML infrastructure companies
Benefits:
- Proven performance improvements
- Patent-protected innovation
- Extensive documentation
- Active development community
- Technical support available
Explore Licensing Opportunities
🤝 Industry Partnership Opportunities
Technology Licensing
Integrate LABIOS into your products with our flexible licensing options.
- ✓ Exclusive or non-exclusive licenses
- ✓ Royalty or fixed-fee structures
- ✓ Technical support packages
Research Collaboration
Partner with our team to advance the state of the art in I/O systems.
- ✓ Joint R&D projects
- ✓ Student internship programs
- ✓ Co-authored publications
Custom Solutions
Work with us to tailor LABIOS for your specific use cases.
- ✓ Architecture consultation
- ✓ Performance optimization
- ✓ Integration assistance
Start the Conversation
Join leading organizations leveraging LABIOS to transform their data infrastructure. Let's discuss how LABIOS can accelerate your innovation.
[Contact Partnership Team](mailto:akougkas@illinoistech.edu?subject=LABIOS Partnership Inquiry) | Schedule a Demo
Join the LABIOS Community
Connect with researchers and developers working on next-generation I/O systems
Join Zulip Chat | Contact Team
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
What makes LABIOS different from existing I/O systems?
LABIOS introduces a unified label abstraction that works across HPC, Big Data, and AI workloads. Unlike traditional systems optimized for specific use cases, LABIOS adapts dynamically to different I/O patterns while maintaining high performance.
How does licensing work for commercial use?
LABIOS is available under a dual licensing model. The core technology is open source for research use, while commercial deployments require a license through IIT's technology transfer office. Contact us for specific terms and pricing.
Can LABIOS integrate with my existing storage infrastructure?
Yes! LABIOS is designed as a middleware layer that works with existing storage systems including parallel file systems (Lustre, GPFS), object stores (S3, Swift), and local storage (NVMe, SSD). No infrastructure changes required.
What performance improvements can I expect?
Performance gains vary by workload, but typical improvements include: 2-6x I/O throughput, 10x reduction in tail latency, 3x memory savings for GPU workloads, and 40% overall application speedup for I/O-intensive applications.
Is LABIOS production-ready?
Yes! LABIOS has been validated in production environments at DOE national laboratories and is currently at Technology Readiness Level 6. Version 2.0 (coming in 2026) will include additional enterprise features.
How do I get started with LABIOS?
Start with our GitHub repository and documentation. For production deployments, we recommend contacting our team for architecture review and optimization guidance. Training and support packages are available.
Have more questions?
Email Technical Team | Join Community Chat
🙏 Acknowledgments
❤️ Funding Support
National Science Foundation
Award #2331480
Primary funding enabling LABIOS research and development
👥 Research Partners
DOE National Laboratories
Argonne • Lawrence Livermore • Sandia
NSF Cyberinfrastructure
Delta • Chameleon • CloudLab
Collaborative partnerships advancing storage innovation
LABIOS is developed at the Gnosis Research Center, Illinois Institute of Technology
NSF Award #2331480
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 2331480. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
LABIOS is protected under U.S. Patent 11,630,834 B2. Commercial use requires licensing through Illinois Institute of Technology's Office of Technology Development.