IOWarp: Advanced Data Management Platform for AI-Augmented Scientific Workflows
IOWarp is a $5 million NSF-funded platform (Award #2411318, 2024-2029) that provides proven infrastructure for intelligent I/O orchestration in scientific computing. IOWarp is a comprehensive data management platform designed to address the unique challenges in scientific workflows that integrate simulation, analytics, and Artificial Intelligence (AI). IOWarp builds on existing storage infrastructures, optimizing data flow and providing a scalable, adaptable platform for managing diverse data needs in modern scientific workflows, particularly those augmented by AI.
Project Scope and Vision
Project Goals
IOWarp focuses on:
- Enhancing data exchange and transformation across scientific workflows.
- Reducing data access latency with advanced storage systems.
- Developing an open-source, community-driven framework that supports adaptability and innovation.
Vision
IOWarp envisions a modular and flexible architecture that adapts to the data demands of scientific research, particularly in High-Performance Computing (HPC). This platform aligns with NSF's focus on sustainable, adaptable solutions that can support next-generation scientific workflows.
Key Challenges in Scientific Data Management
- Data Heterogeneity: Managing a variety of data formats across workflow stages.
- Data Scale: Addressing the rapidly increasing volume and velocity of data.
- Data Access Speed: Overcoming limitations in I/O speed for real-time analytics.
- Data Integrity: Ensuring quality and consistency across storage and access points.
- Resource Utilization: Optimizing storage and compute resources to reduce costs and environmental impact.
- Interoperability: Enabling seamless data transfer across workflow stages and computing paradigms.
From Current State to IOWarp: The Transformation
IOWarp transforms how scientific data flows through modern HPC systems by introducing intelligent orchestration across the entire storage hierarchy.
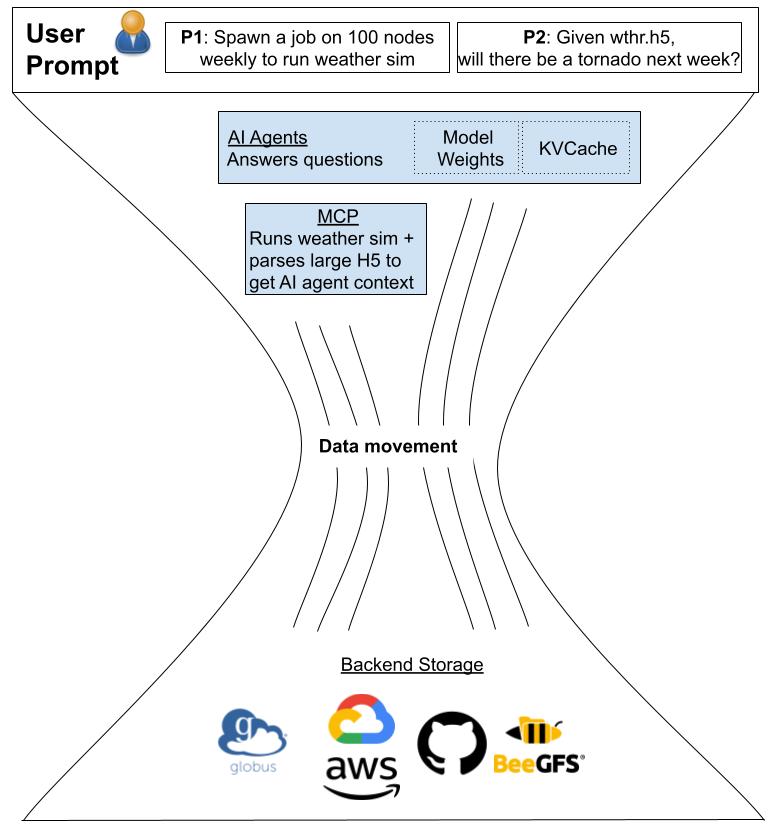
Current State
Traditional parallel file system architecture with limited data management capabilities
Future State with IOWarp
IOWarp-enhanced architecture with intelligent data orchestration and AI integration
Traditional systems rely on manual data management and static storage hierarchies, leading to inefficient data movement and underutilized resources. IOWarp introduces intelligent, automated data orchestration that adapts to workflow demands, dramatically improving performance and resource utilization.
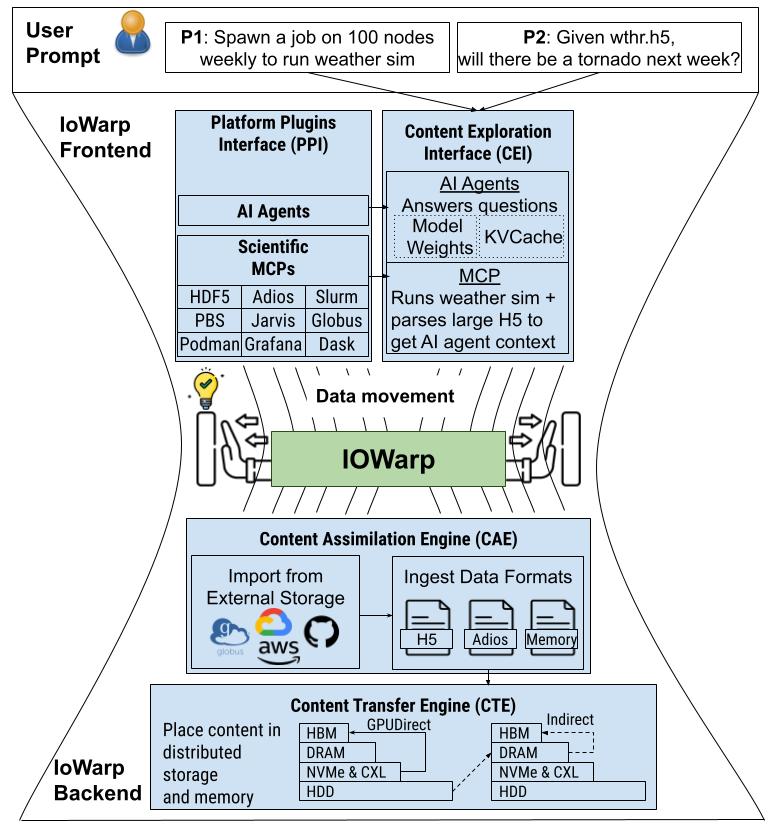
Architecture
Modular Architecture
IOWarp's architecture comprises several core components designed to handle various aspects of data flow, integrity, and interoperability.
Technical Architecture
This section describes the core components of IOWarp's data management platform and their functionality within scientific workflows.
Content Assimilation Engine (CAE)
The Content Assimilation Engine (CAE) transforms diverse format-specific data into IOWarp's unified data representation format, Content, optimized for data transfer. The CAE:
- Integrates with data sources (e.g., Globus, S3, PFS).
- Applies data layout and semantic tagging, preserving context across workflow stages.
- Exports data back to repositories post-processing, ensuring data longevity.
Content Transfer Engine (CTE)
The Content Transfer Engine (CTE) manages efficient data flow across workflow stages and storage systems.
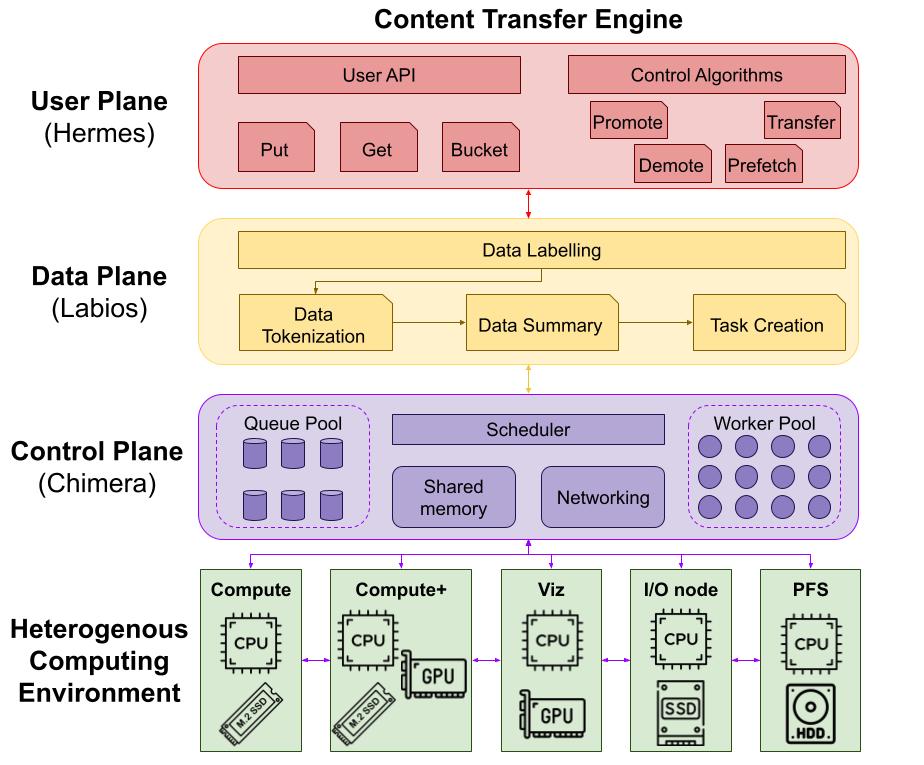
CTE architecture with LabIOS integration for multi-tiered storage management
Key features include:
- Multi-tiered I/O: Supports interactions with advanced storage hardware, including NVMe SSDs and CXL-powered devices.
- GPU Direct I/O: Directly transfers data between GPUs for faster model training and inference.
- Secure Transfer Protocols: Ensures data security during transfers.
Content Exploration Interface (CEI)
The Content Exploration Interface (CEI) enables advanced data querying and retrieval, incorporating tools like:
-ce4c91d084e364c52206b2af25a0e842.png)
CEI architecture showing natural language query processing and integration
- WarpGPT: A language model-driven interface for complex scientific queries, capable of handling anomaly detection, mathematical operations, and user-defined extensions.
- FAIR Compliance: Implements principles to support Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable data within scientific workflows.
Platform Plugins Interface (PPI)
The Platform Plugins Interface (PPI) extends IOWarp's functionality, allowing integration with external services, such as:
- Global Schedulers (e.g., Slurm): For resource and task allocation.
- Workflow Managers (e.g., Pegasus): For task orchestration and system telemetry.
- Custom Libraries: Allows integration with libraries for data tracing, encryption, and transformations.
High-Level Data Flow in IOWarp
The data flow within IOWarp follows an organized pipeline from acquisition and transformation to storage and retrieval. Here's a typical data path:
- Data Ingestion via the Content Assimilation Engine.
- Data Storage Optimization through the Content Transfer Engine and hardware-optimized storage.
- Data Retrieval using the Content Exploration Interface, with support for complex, low-latency queries.
API Descriptions
Core APIs
-
Repository Connection API: Manages connection to external data sources.
- Example Methods:
link/unlink,upload/download.
- Example Methods:
-
Content Management API: Allows querying, editing, and locating content based on metadata and tags.
- Example Methods:
queryContent,editContent.
- Example Methods:
-
Content Exploration API: Supports advanced data operations with low-latency retrieval.
- Example Methods:
processQuery,executeDAG.
- Example Methods:
-
AI/ML Integration APIs: Facilitates data exchange for training and inference tasks within AI frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch.
- Example Methods:
defineDataset,prefetchToGPU.
- Example Methods:
Towards Agentic-Driven Scientific Workflows
Modern scientific computing is evolving towards agentic-driven workflows, where AI agents autonomously orchestrate complex computational tasks, interact with scientific data, and manage HPC resources through natural language interfaces. IOWarp is at the forefront of this transformation, providing the infrastructure and tools necessary to enable intelligent, automated scientific discovery.
Our work on agentic-driven scientific workloads includes the development of Warpio CLI and integration with Model Context Protocols (MCPs), enabling researchers to interact with HPC systems, scientific data formats, and computational workflows using natural language and AI-powered assistance.
Warpio CLI: Command-line interface for agentic scientific workflows
AI Agents for Scientific Computing
Following Anthropic's November 2024 release of the Model Context Protocol (MCP), IOWarp has pioneered the integration of AI agents into scientific computing environments. These agents can:
- Understand Scientific Data: Parse and analyze data from formats like HDF5, Adios BP5, NetCDF
- Orchestrate Workflows: Submit jobs, manage resources, and coordinate multi-step computational pipelines
- Generate Insights: Perform data analysis, create visualizations, and answer scientific queries
- Ensure Reproducibility: Track provenance and enable replay of complex workflows
Model Context Protocols for Science
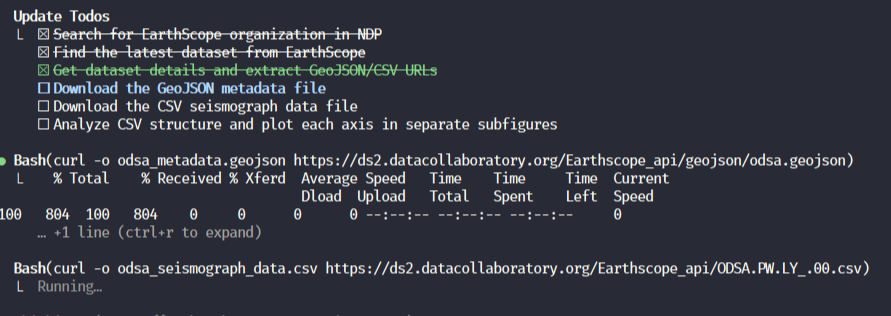
Warpio accessing the National Data Platform to download and analyze the latest EarthScope seismological datasets
IOWarp provides a growing collection of scientific MCPs available at github.com/iowarp/iowarp-mcps. Some examples include:
- Adios MCP: Analyze and query Adios BP5 files from simulations like LAMMPS, WRF, and more
- HDF5 MCP: Explore HDF5 datasets, read metadata, and extract scientific data
- Jarvis MCP: Automated application deployment, environment management, and orchestration
- Slurm MCP: Job scheduling, resource allocation, and queue management
- System Monitoring MCPs: Real-time performance metrics and resource utilization tracking
Scientific Application Examples
IOWarp supports a wide range of scientific applications through its flexible architecture and scientific MCPs, enabling researchers to interact with complex data using natural language.
LAMMPS Molecular Dynamics Simulation
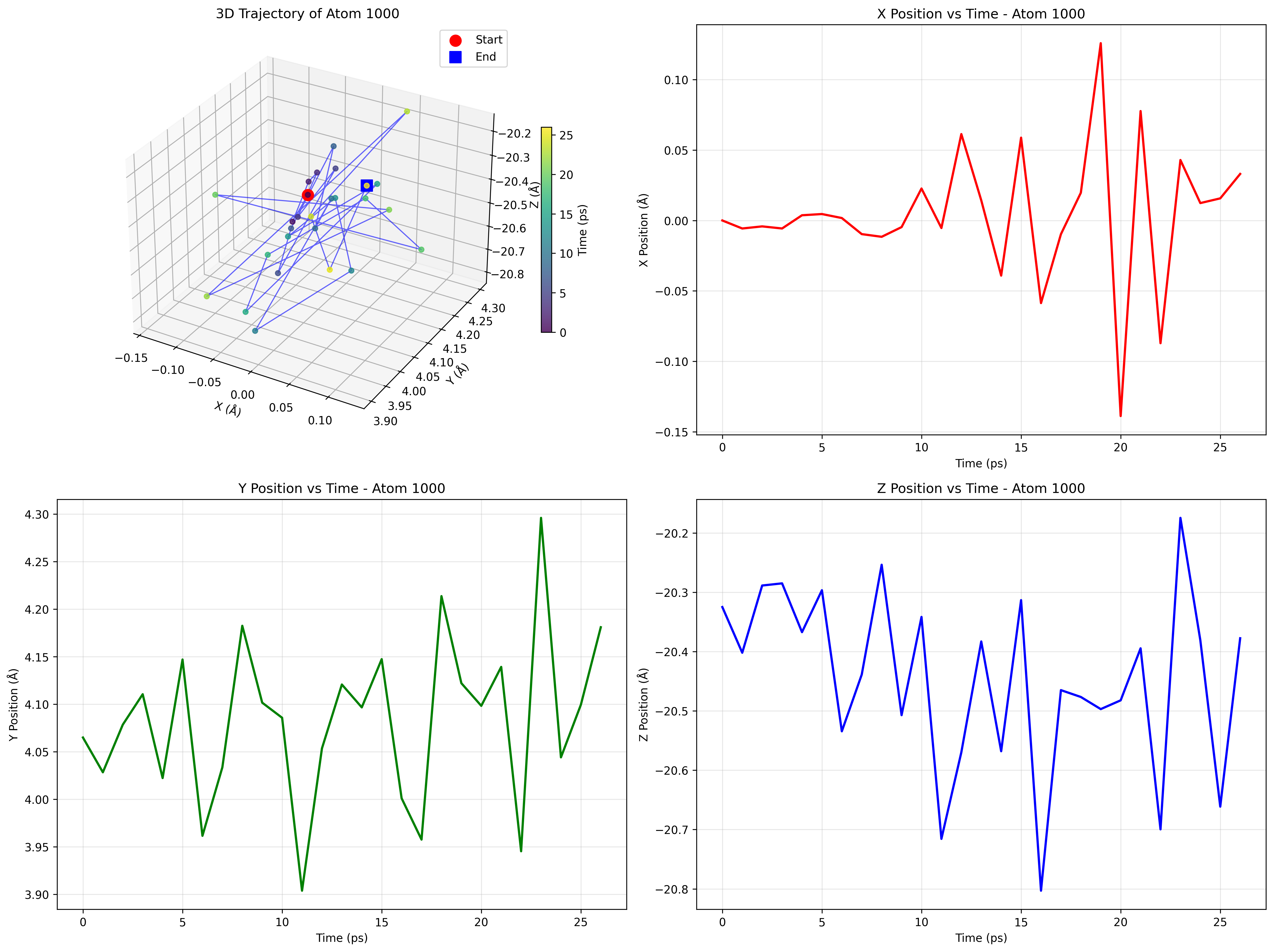
Atom trajectory analysis from LAMMPS simulation
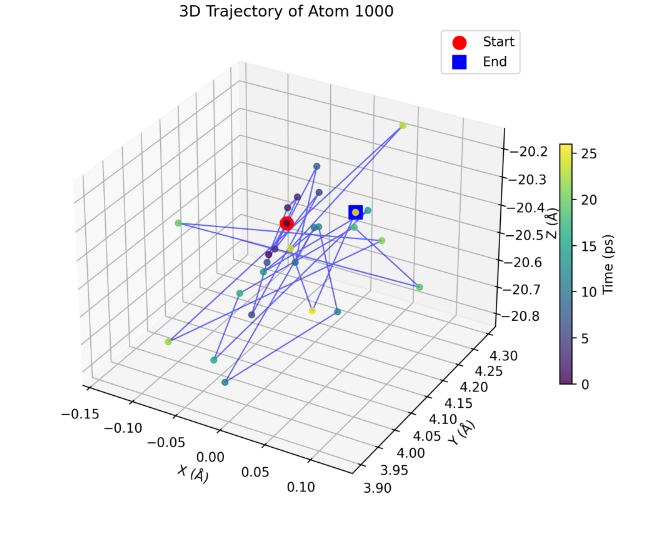
Detailed single-atom trajectory over time
Dataset: LAMMPS molecular dynamics simulation output stored in Adios BP5 format with atom position data over time.
Execution: Agents used Adios-MCP, which provides AI systems with the ability to read and query Adios BP5 files, to analyze the simulation data and generate visualizations.
Prompt: "Can you write me a python script that plots the trajectory of a single atom over time. The atom of choice should be a parameter to the script. The output should be a PNG image with the results. Please run the script for atom 23."
Result: The Adios-MCP enabled the agent to automatically read the BP5 file structure, extract position data for the specified atom, generate Python visualization code, execute the script, and produce the trajectory visualization. This eliminates the need for researchers to manually parse the Adios file format or write custom analysis scripts.
Pipe Flow Data Visualization via ParaView-MCP
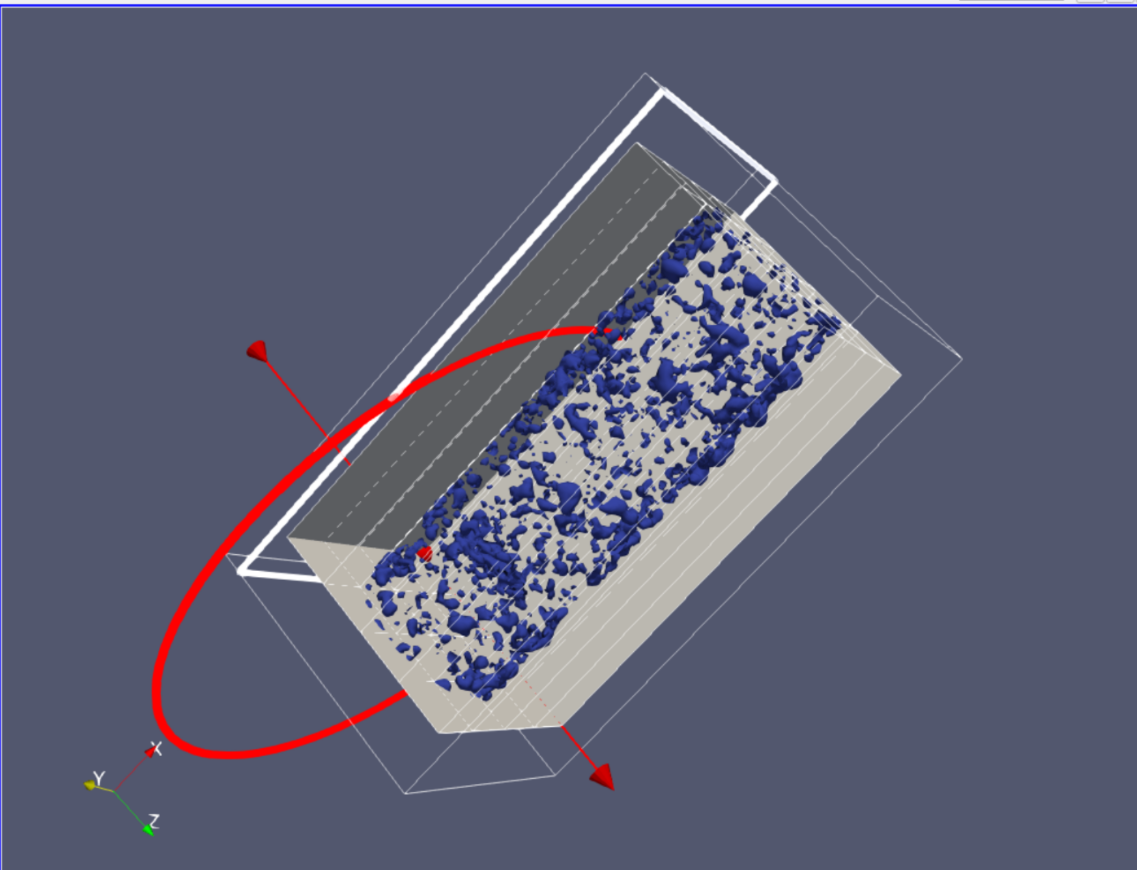
3D flow visualization combining isosurface and orthogonal slice planes generated through natural language commands
Dataset: Incompact3d pipe flow simulation (data.bp5) with pressure and velocity fields.
Execution: Agents used ParaView-MCP, a service that connects AI systems to the ParaView visualization engine, to load the dataset and generate the 3D visualization.
Prompt: "Explore the pipe flow data. Generate an isosurface of pressure at pp=0.1 plus three orthogonal slice planes (X, Y, Z)."
Result: Produced a combined 3D flow visualization without manual setup, highlighting internal flow structures. The ParaView-MCP enabled researchers to create complex visualizations through natural language, eliminating the need for manual ParaView configuration, Python scripting, or format conversion. The agent automatically:
- Loaded the BP5 simulation data
- Generated a pressure isosurface at the specified threshold
- Created three orthogonal cutting planes
- Composed the final visualization showing both surface and volumetric flow features
This demonstrates how IOWarp's MCP ecosystem transforms scientific visualization from a multi-step manual process into a conversational workflow, allowing researchers to focus on interpreting results rather than configuring visualization pipelines.
System Observability & Monitoring
IOWarp provides comprehensive observability features for tracking system performance and resource utilization in real-time.
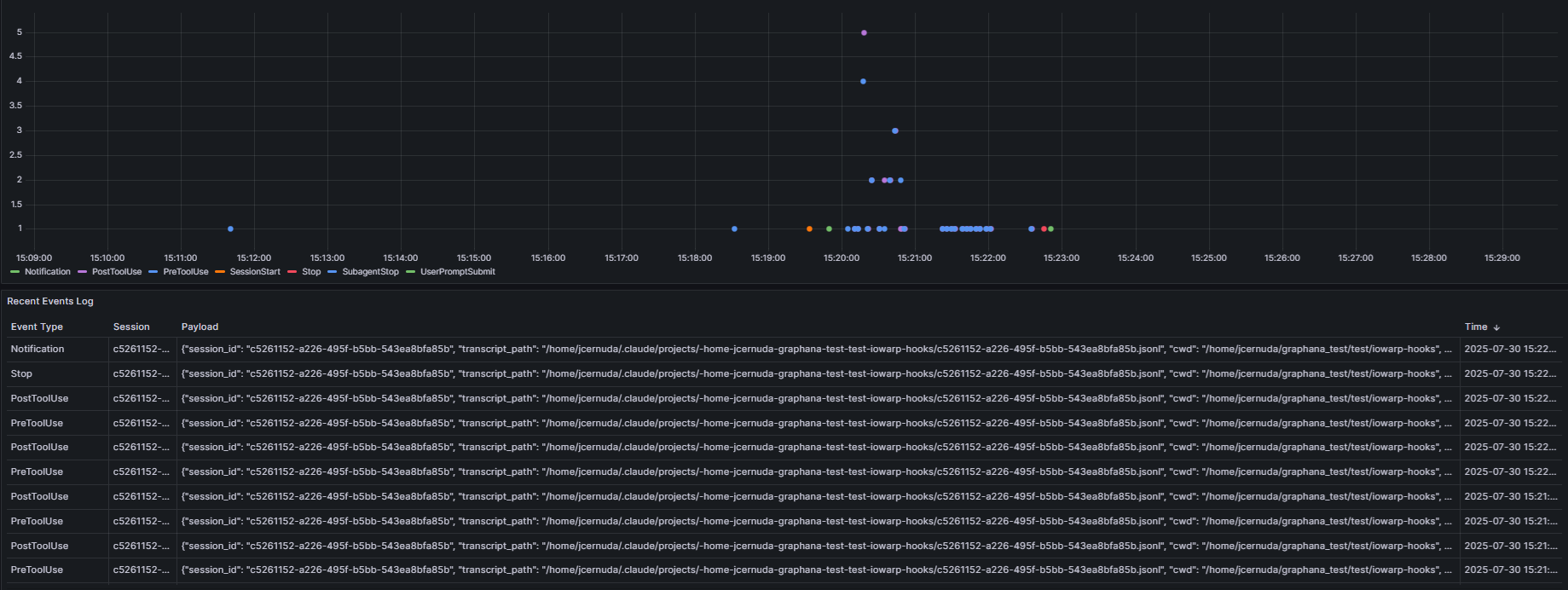
Real-time observability dashboard for monitoring IOWarp performance and resource utilization
Features include:
- Real-time Metrics: Performance tracking across all storage tiers
- Resource Monitoring: DRAM, NVMe, GPU memory, and PFS utilization
- Workflow Visualization: End-to-end workflow execution and bottleneck identification
- Reproducibility Tracking: Full provenance capture for agentic workflows
Performance Results & Benchmarks
We evaluated ContextWarp (IOWarp's agentic framework) across multiple dimensions to understand the performance, correctness, and reliability of AI-driven scientific workflows. Experiments were conducted on Chameleon Cloud using compute nodes with 40GB A100 GPUs.
Agentic Workflow Performance: EarthScope Dataset Analysis
Experiment: Automated download and visualization of seismological data from the National Data Platform using AI agents.
Setup: Claude Code with Sonnet 4 model, with and without IOWarp Context (MCPs and machine configuration).
Task: "Use the ndp mcp to find the latest dataset of the earthscope organization, find the url of the geojson and csv they contain, and download them. The geojson is metadata, the csv contains seismograph data. Plot a figure containing the data of each axis on their own subfigure."
Results:
- With IOWarp Context: Successfully completed in 2 minutes with correct tool selection and visualization
- Without IOWarp Context: Failed to execute (agent could not identify correct tools or access methods)
- Manual Process: ~15 minutes (login, search, download, build visualization script)
- Speedup: 7.5x faster than manual workflow
This demonstrates that IOWarp Context (MCPs + system prompts) is essential for enabling AI agents to interact with scientific infrastructure effectively.
Agent Configuration Performance: Jarvis IOR Deployment
We compared eight agent-model combinations deploying the IOR parallel I/O benchmark using Jarvis (IOWarp's deployment automation system) across five distinct prompts to assess performance and correctness tradeoffs.
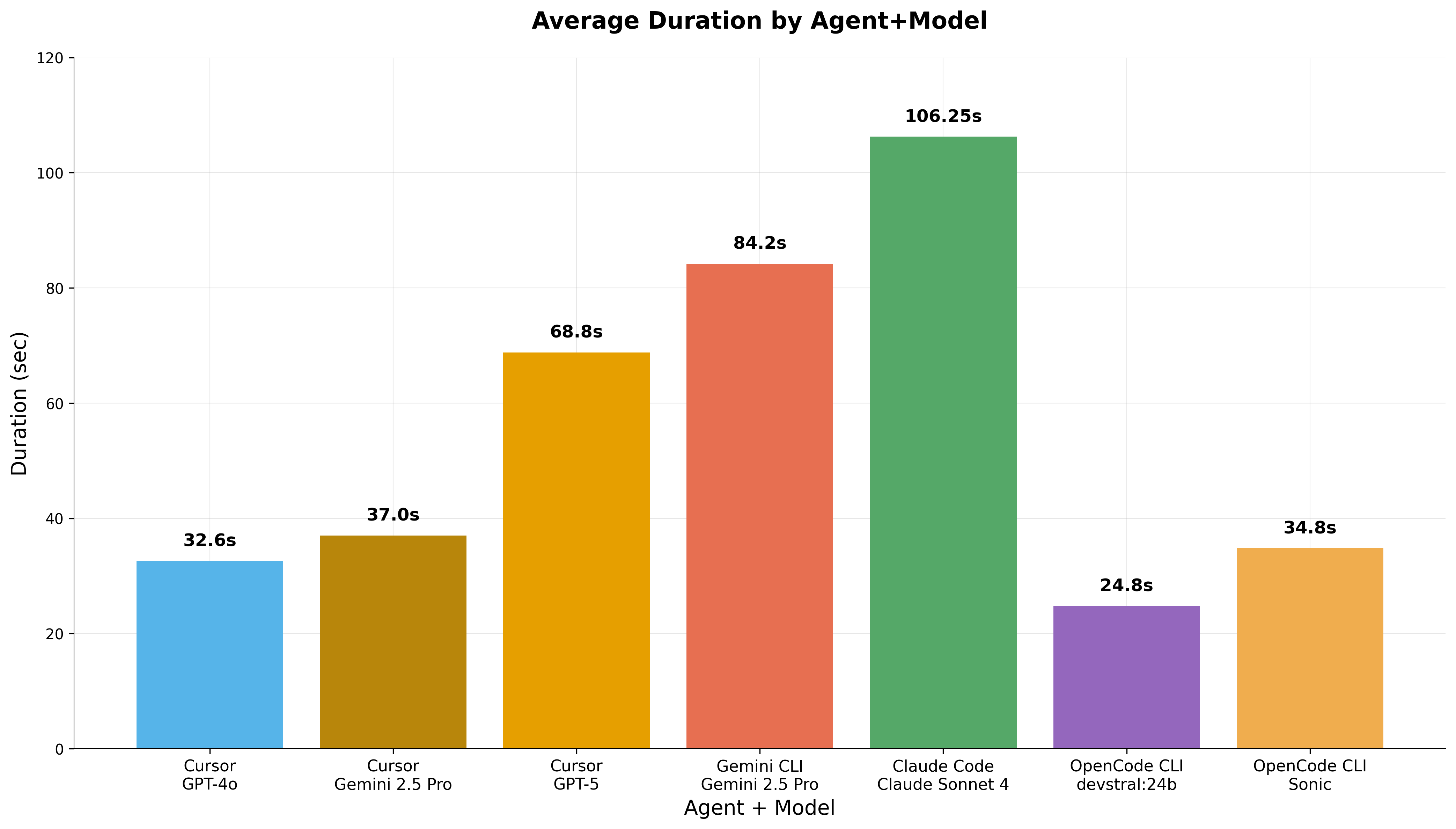
Execution time comparison across different agent and model configurations
Execution Time Results (average across 5 prompts):
- OpenCode + Devstral (local LLM for execution): 24.8 seconds (fastest)
- Cursor + GPT-4o: 37.7 seconds
- Gemini CLI + Gemini 2.5 Pro: 85.9 seconds
- Claude Code + Sonnet 4: 109.2 seconds
Key Finding: Agents using small, self-hosted LLMs for execution (like Devstral) with large cloud models only for planning achieved competitive or superior performance compared to using large models for all operations. This validates IOWarp's split planning-execution design for efficiency, cost reduction, and data security.
Tool Call Success Rates
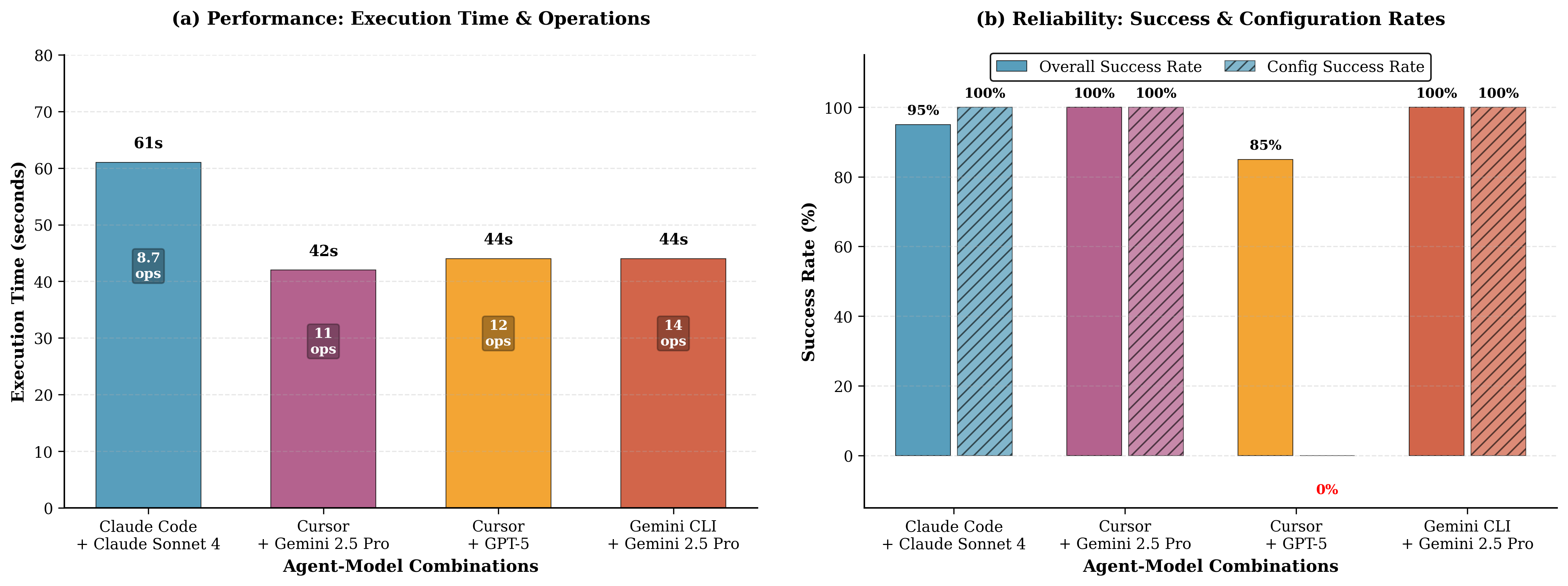
Success rates for correctly identifying and invoking scientific tools across agent-model combinations
Robustness Across Diverse Prompts
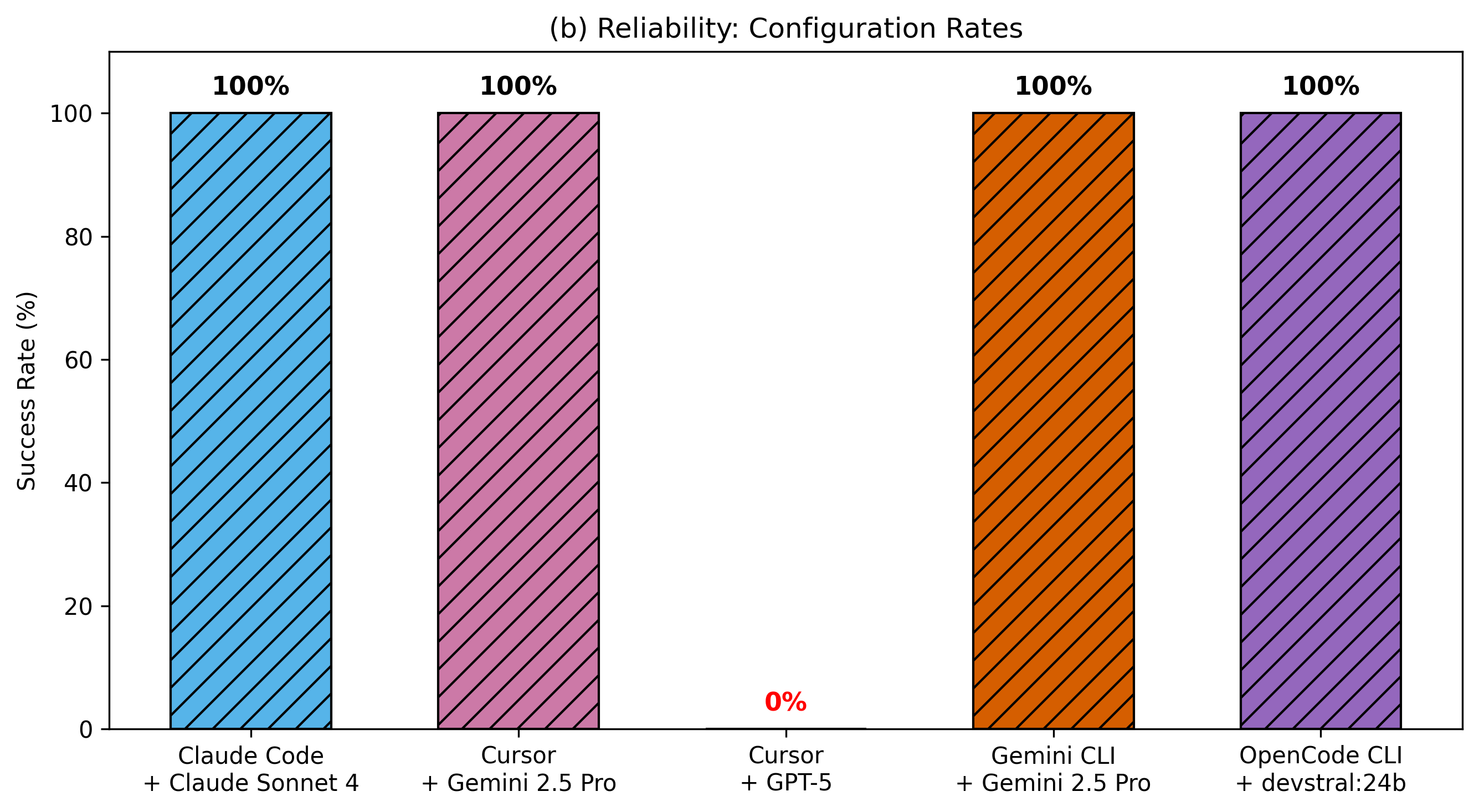
Configuration success rates when tested with 20 different prompt styles ranging from simple to highly detailed
Robustness Test: 20 prompts with varying detail levels for IOR deployment, from simple ("Deploy ior with 8 processes using the deployment agent") to detailed bash scripts.
Configuration Success Rates (20 prompts):
- Claude Code + Sonnet 4: 100%
- Gemini CLI + Gemini 2.5 Pro: 100%
- OpenCode CLI + Gemini 2.5 Pro: 100%
- OpenCode CLI + Devstral-2hl: 100%
- Cursor + GPT-5: Lower success rate (struggled with parameter synonyms like "nprocs" vs "number of processes")
Key Finding: IOWarp's agentic design is highly resilient to changes in prompt phrasing and information granularity. Configurations using local LLMs for execution achieved 100% success, demonstrating that the split plan-execution architecture effectively balances cost, security, and reliability.
Demonstrations
IOWarp-MCP Demo
Full workflow showcase from scheduling to deployment, data collection, and analysis using IOWarp MCPs with Claude Code.
IOWarp Reproducibility Demo
Showcase of IOWarp's reproducibility visualizer for agentic workflows, enabling full provenance tracking and replay.
IOWarp-MCP Adios Demo
Showcase of IOWarp Adios MCP providing full analysis of a BP5 file generated by LAMMPS, demonstrating natural language queries on scientific data.
Publications
Authors | Title | Venue | Type | Date | Links |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| , , , , | Stimulus: Accelerate Data Management for Scientific AI applications in HPC | The 22nd IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Internet Computing (CCGRID'22), May 16-19, 2022 | Conference | May, 2022 | |
| , , , , , , , | HFlow: A Dynamic and Elastic Multi-Layered Data Forwarder | The 2021 IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing (CLUSTER'21), September 7-10, 2021 | Conference | September, 2021 | |
| , , , , , , , | Apollo: An ML-assisted Real-Time Storage Resource Observer | The 30th ACM International Symposium on High-Performance Parallel and Distributed Computing (HPDC'21), June 21-25, 2021 | Conference | June, 2021 | |
| , , , , | DLIO: A Data-Centric Benchmark for Scientific Deep Learning Applications | The 2021 IEEE/ACM International Symposium in Cluster, Cloud, and Internet Computing (CCGrid'21), May 17 - 20, 2021 Best paper award | Conference | May, 2021 | |
| , , | HReplica: A Dynamic Data Replication Engine with Adaptive Compression for Multi-Tiered Storage | The 2020 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data'20), December 10-13, 2020 | Conference | December, 2020 | |
| , , | A Dynamic Multi-Tiered Storage System for Extreme Scale Computing | The International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis (SC'20) | Poster | November, 2020 | |
| , , , | HCL: Distributing Parallel Data Structures in Extreme Scales | IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing (CLUSTER'20), Sept. 14-17, 2020 | Conference | September, 2020 | |
| , , , | HCompress: Hierarchical Data Compression for Multi-Tiered Storage Environments | IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium (IPDPS'20), May 18-22, 2020 | Conference | May, 2020 | |
| , , | HFetch: Hierarchical Data Prefetching for Scientific Workflows in Multi-Tiered Storage Environments | IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium (IPDPS'20), May 18-22, 2020 | Conference | May, 2020 | |
| , , | I/O Acceleration via Multi-Tiered Data Buffering and Prefetching | Journal of Computer Science and Technology (JCST'20), vol 35. no 1. pp 92-120 | Journal | January, 2020 | |
| , , | HFetch: Hierarchical Data Prefetching in Multi-Tiered Storage Environments | The International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis (SC'19) Best Poster Nominee, Ph.D Forum | Poster | November, 2019 | |
| , , , | LABIOS: A Distributed Label-Based I/O System | The 28th International Symposium on High-Performance Parallel and Distributed Computing (HPDC'19), Phoenix, USA 2019. pp. 13-24. Karsten Schwan Best Paper Award | Conference | June, 2019 | |
| , , | An Intelligent, Adaptive, and Flexible Data Compression Framework | IEEE/ACM International Symposium in Cluster, Cloud, and Grid Computing (CCGrid'19), Larnaca, Cyprus2019. pp. 82-91. | Conference | May, 2019 | |
| , , , | Vidya: Performing Code-Block I/O Characterization for Data Access Optimization | The IEEE International Conference on High Performance Computing, Data, and Analytics 2018 (HiPC'18), Bengaluru, India2018. pp. 255-264. | Conference | December, 2018 | |
| , , , | Harmonia: An Interference-Aware Dynamic I/O Scheduler for Shared Non-Volatile Burst Buffers | The IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing 2018 (Cluster'18), Belfast, UK2018. pp. 290-301. | Conference | September, 2018 | |
| , , | Hermes: A Heterogeneous-Aware Multi-Tiered Distributed I/O Buffering System | The 27th ACM International Symposium on High-Performance Parallel and Distributed Computing (HPDC), Tempe, AZ, USA, 2018. pp. 219-230 | Conference | June, 2018 |
Resources & Links
- GitHub Organization: github.com/iowarp
- IOWarp MCPs: github.com/iowarp/iowarp-mcps
- Documentation: IOWarp Tutorial
Collaborators

HDF Group

University of Utah
Deployment Partners
IOWarp is deployed and being evaluated at leading national laboratories:
- Argonne National Laboratory - Advanced computing research and leadership computing facilities
- Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory - High-performance computing systems and simulation science
- NERSC (National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center) - DOE scientific computing facility
Sponsor

National Science Foundation
Award #2411318 (2024-2029)
$5 Million
