
DTIO: A Data Task I/O Runtime
In partnership with Argonne National Laboratory, DTIO investigates the use of a task framework for unifying complex I/O stacks and providing features such as resilience, fault-tolerance, and task replay.
Introduction: What is DTIO?
- Converged workflows that combine HPC, Big Data and ML tasks need to compute intermediate results and share them at large scale.
- HPC, Big Data Analytics, and ML feature a variety of data formats, data models, and semantics, as well as I/O libraries that implement them.
- These all need to interact with each other, while managing requirements with different benefits and limitations.
- DTIO is a scalable I/O runtime that unifies the disparate data stack for modern scientific and ML workflows.
- DTIO provides a DataTask Abstraction that enables transformation and unification of data formats across HPC, Big Data, and ML, as well as unique I/O pipeline optimizations.
- Insight: DTIO's task-based infrastructure gives several advantages over a batch-based infrastructure, which can also apply to I/O tasks.
- Improved scalability via relaxation of POSIX consistency, which allows tasks to execute faster even if it disobeys strict ordering.
- Improved resource utilization via constraint-based task scheduling, which allows tasks to consider load on an executor.
- Improved fault-tolerance via task provenance, which allows replay of tasks in the event of a fault.
- In addition, we aim to leverage hierarchical storage and computational storage techniques to provide an infrastructure that unifies and extends the current I/O stacks.
Methodology
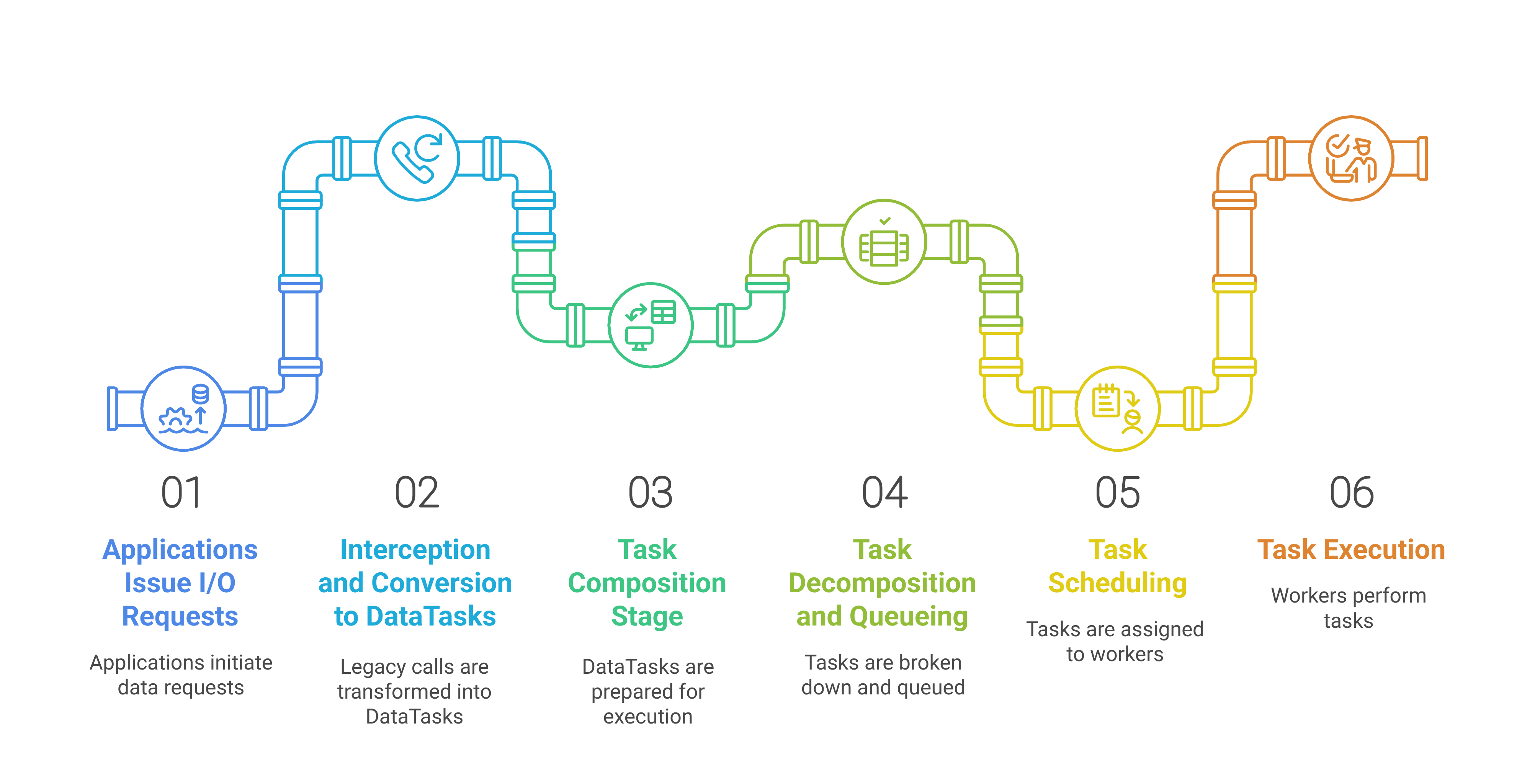
- DTIO's has a six-stage I/O processing pipeline:
- (1) Applications initiate I/O requests
- (2) Legacy I/O calls are intercepted and converted into DataTasks
- (3) DataTasks are prepared for execution during the Task Composition stage
- (4) Tasks are decomposed and queued
- (5) Tasks are scheduled and assigned to executors
- (6) Executors perform the I/O operations.
Accelerated I/O Resolution Optimization
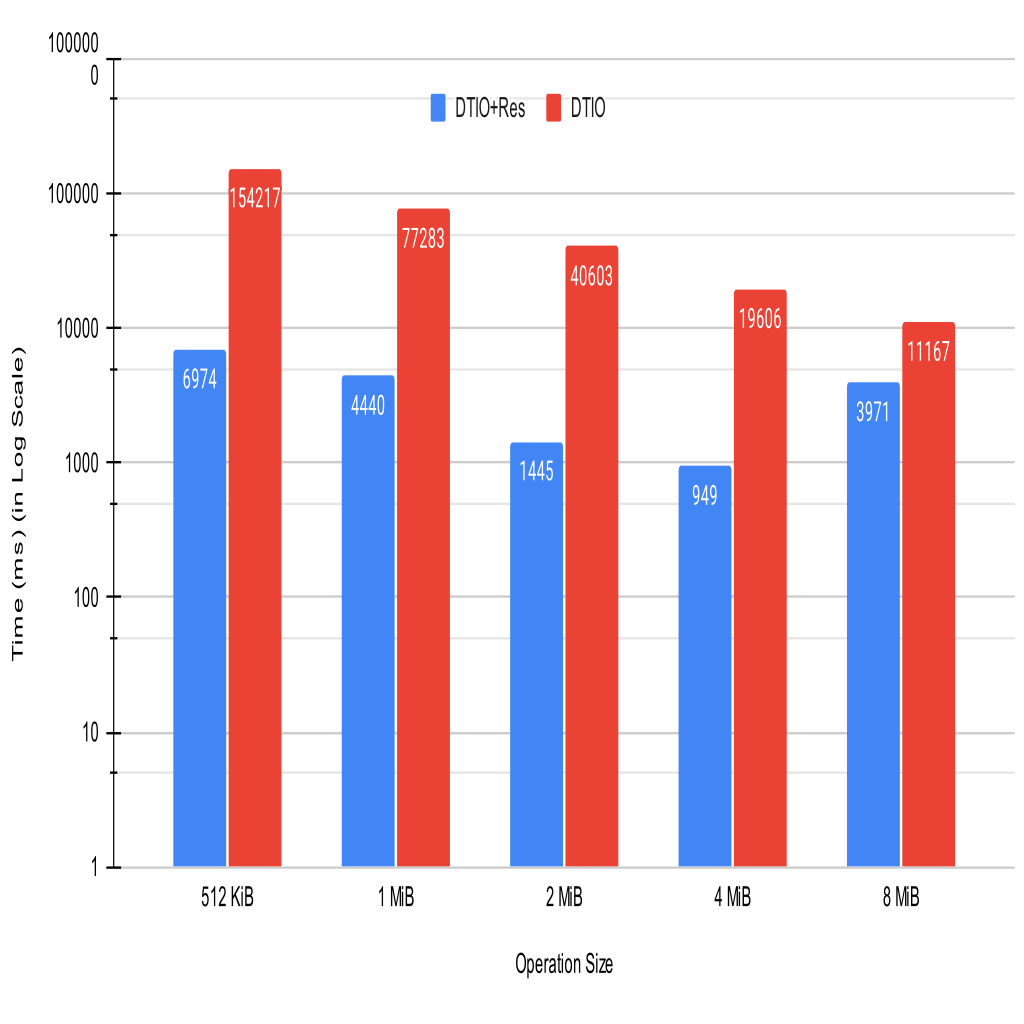
- DTIO implements an Accelerated I/O resolution optimization, which temporarily stores DataTasks in a circular buffer so that subsequent DataTasks can retrieve data directly from local memory.
- The read performance demonstrates a reduction in read time by 95.5% at 512 KiB with accelerated resolution and 64.4% reduction at 8 MiB, for an average reduction of 89.2%.
- The overhead for this is minimal, with a worst-case of 12% overhead on writes.
Data Staging and Prefetching Techniques
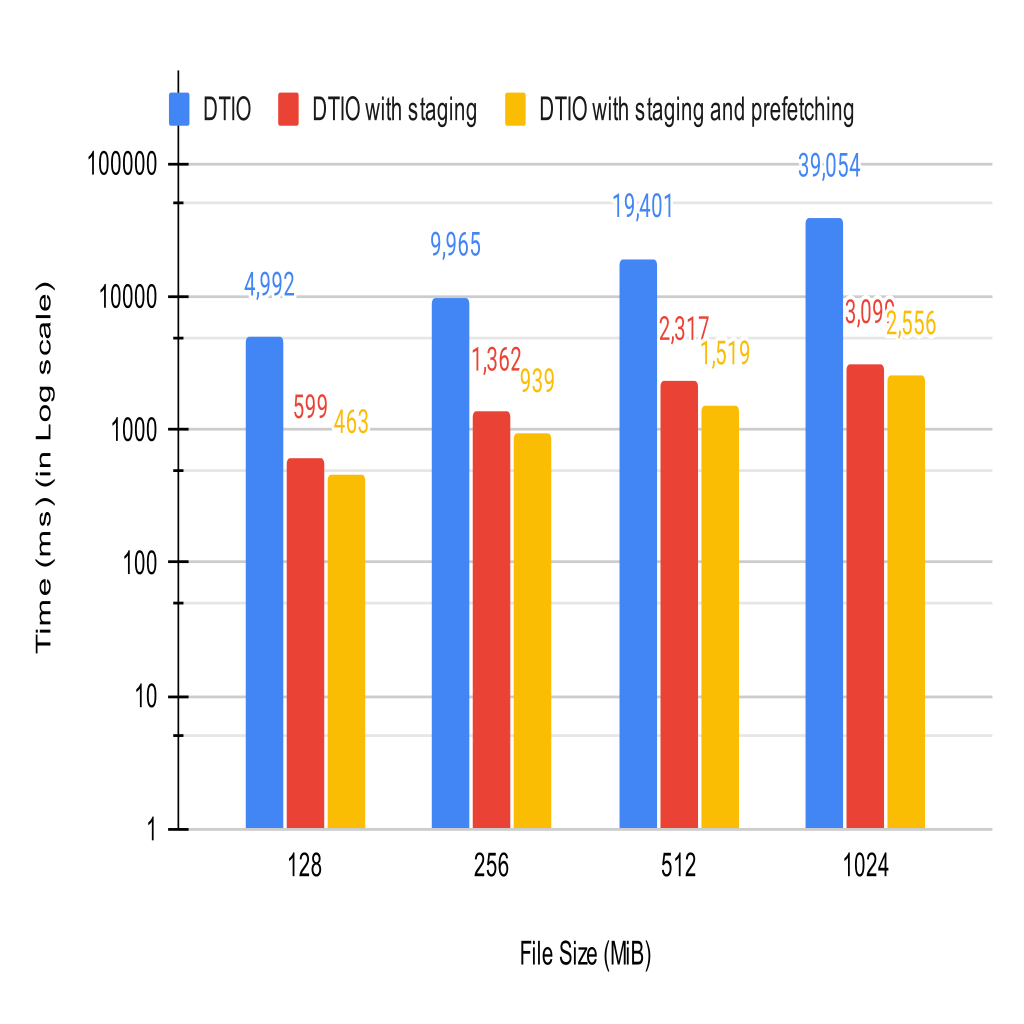
- DTIO implements a data policy that allows DataTask Executors to stage data pre-emptively before read operations arrive for it.
- In addition to this policy, DTIO can also send the data to the circular buffers of the clients asynchronously so that it can be accessed locally.
- The performance of the staging optimization shows an improvement of 88.6% over DTIO without staging. Adding the prefetching optimization to staging improves performance by a further 3.1%, total of 91.7%.
End-to-End Results with PtychoNN Application
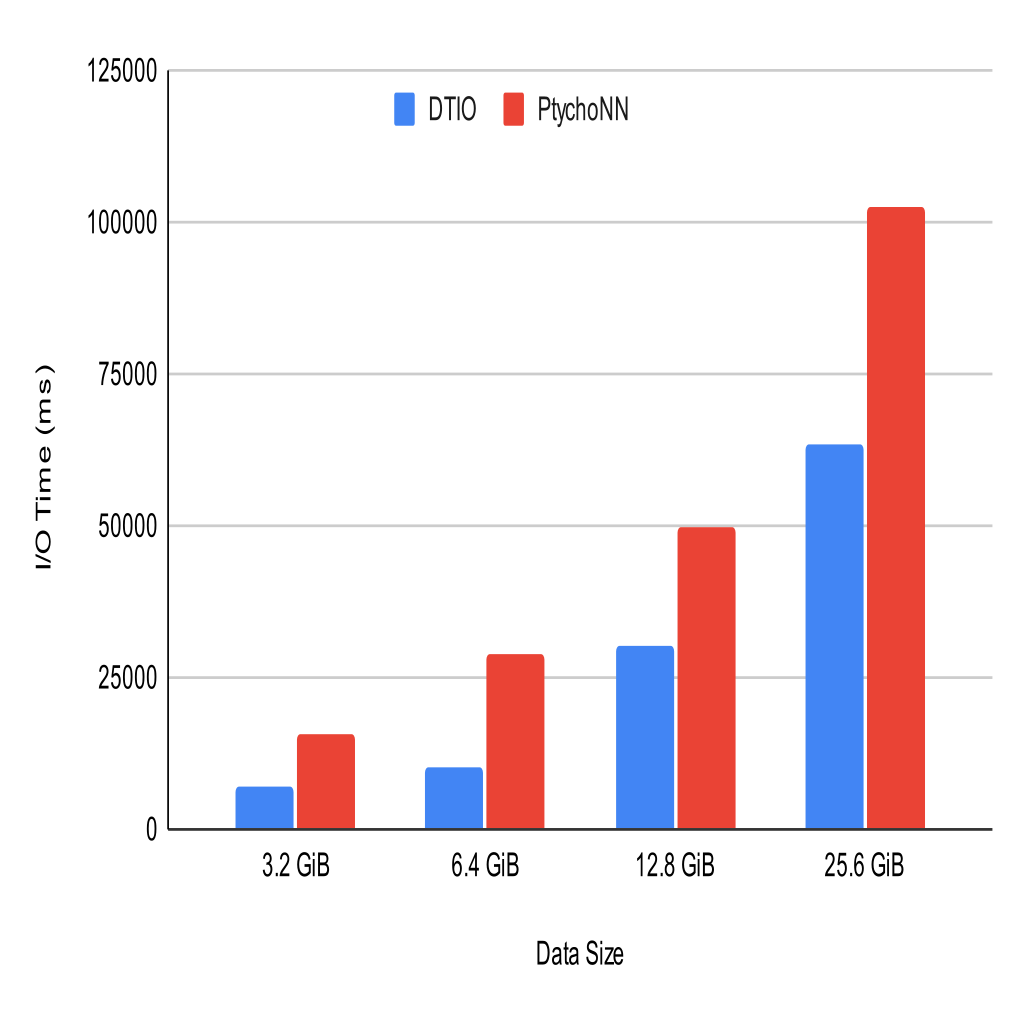
- The PtychoNN workflow consists of a producer which reads in HDF5 data and converts it to Numpy and a consumer which reads the Numpy data as tensors. With DTIO acting as an intermediary, the producer and consumer can be run at the same time (as DTIO will allow access to partial results).
- The figure shows the I/O time to run PtychoNN with and without DTIO. In this case, DTIO shows a performance improvement over PtychoNN that varies from 38% for large I/O (25.6 GiB) to 65% for smaller workloads (6.4 GiB). The average I/O performance improvement is 49.6%, or 21.6 seconds of PtychoNN's I/O time.