CCGRID'24 Keynote Review
From May 6 to May 9, 2024, the IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud, and Internet Computing (CCGRID) was held in Philadelphia, USA. On May 7, Professor Xian-He Sun, a distinguished professor at the Illinois Institute of Technology (IIT) and director of the Gnosis Research Center, delivered a keynote titled "AI & Data: Challenges and Opportunities in Computer System Research."

In his keynote, Professor Sun addressed the complex challenges and emerging opportunities in computer system design brought about by the era of AI and big data. He highlighted the scalability issues caused by data access performance bottlenecks in current computer systems. This storage wall has led to a new performance analysis framework that prioritizes data throughput over floating-point computation.
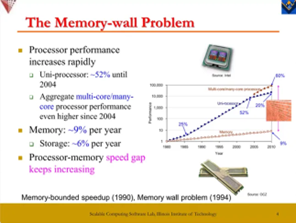
Professor Sun emphasized that data systems are inherently more complex than computing systems. It was discussed the necessity of comprehensive redesigns and optimizations across operating systems, compilers, and hardware which must be designed to fully exploit emerging hardware technologies by making use of optimization methods such as data tiering, compression, indexing, and prefetching. Only through new architectures and performance models can future HPC systems mitigate the "storage wall" performance bottleneck in AI and big data computing.
He highlighted how these new challenges present fundamental research tasks, and opportunities for computer scientists and engineers. To emphasizes these opportunities, Professor Sun highlighted some of the research performed here at the Gnosis Research Center:
- Concurrent Average Memory Access Time (C-AMAT) Model: This model accurately reflects memory performance in modern high-performance computing systems, emphasizing the importance of addressing unhidden miss penalties in high concurrency storage operations.
- Layered Performance Matching (LPM): A method for optimizing storage systems to achieve near-cache performance with large capacity. This method is implemented in the Hermes data input/output hierarchical management system, which significantly enhances performance in scientific computing, big data applications, cloud computing, and deep learning.
- Hermes: Supported by the National Science Foundation, Hermes leverages the C-AMAT model and LPM method, utilizing new storage technologies like NVRAM to enhance performance by 2-3 times. Hermes's success has led to collaboration projects such as ChronoLog, Coeus, and DTIO.
Professor Sun's team continues to optimize storage systems to enhance performance across various computing fields, reflecting the significant shift from computation-centric to data-centric computing. This ongoing work is essential in addressing the evolving needs of AI and big data applications, presenting substantial and ongoing challenges for computer scientists and engineers.
